How MetadataAI™ Reads and Writes All Metadata Types — Seamlessly
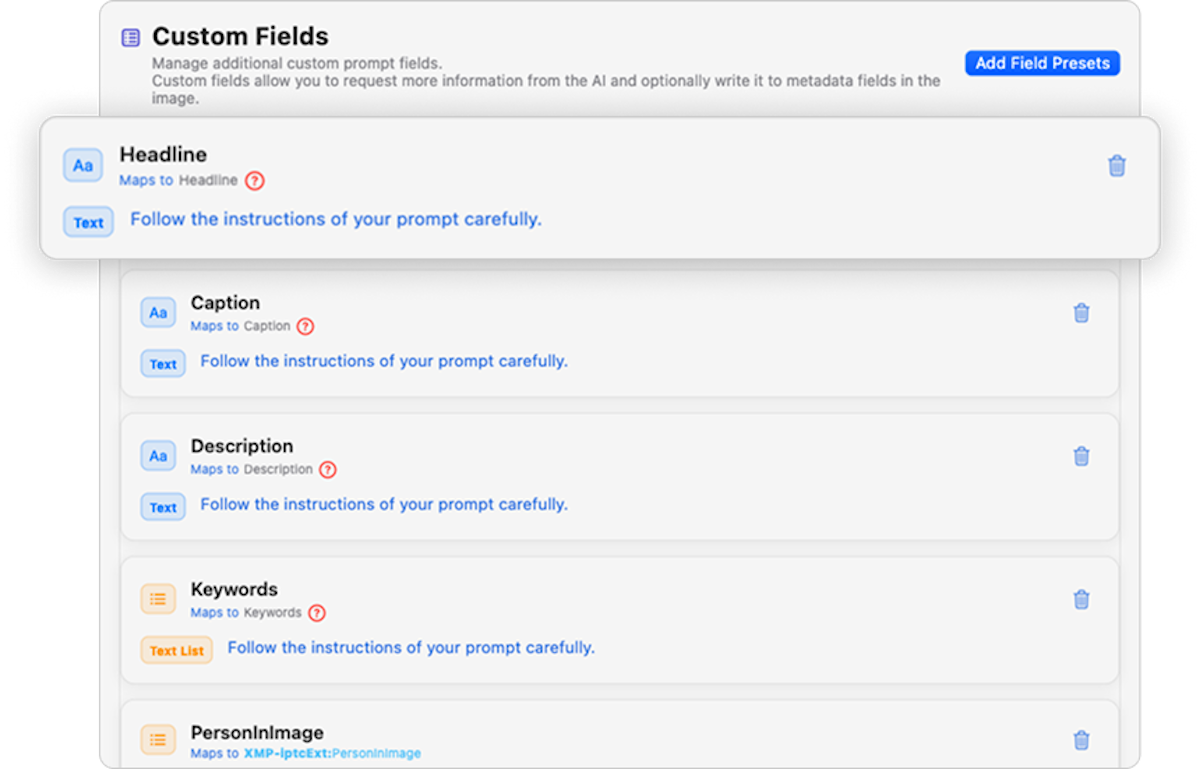
MetadataAI Doesn’t Just Read Your Metadata — It Understands It
In last week’s kickoff to Series A, we broke down the differences between Exif, IPTC, and XMP metadata — and why they matter. Today, we’re going deeper, tackling the technical heart of MetadataAI™:
How it reads, writes, and synchronizes metadata across all three standards — safely, reliably, and intelligently.
For photographers, editors, archivists, and developers alike, this is one of the most important (and underappreciated) challenges in metadata management. It’s one thing to read metadata — most tools can do that. But it’s another thing entirely to write metadata safely, and to do so in a way that works across all major systems and standards.